CryptoDB
New Constructions of Statistical NIZKs: Dual-Mode DV-NIZKs and More
| Authors: |
- Benoît Libert , CNRS, Laboratoire LIP and ENS de Lyon, Laboratoire LIP (U. Lyon, CNRS, ENSL, Inria, UCBL)
- Alain Passelègue , Inria and ENS de Lyon, Laboratoire LIP (U. Lyon, CNRS, ENSL, Inria, UCBL)
- Hoeteck Wee , CNRS, ENS, PSL
- David J. Wu , University of Virginia
|
| Download: |
- DOI: 10.1007/978-3-030-45727-3_14
(login may be required)
- Search ePrint
- Search Google
|
| Presentation: |
Slides
|
|
Conference:
|
EUROCRYPT 2020
|
| Abstract: |
Non-interactive zero-knowledge proofs (NIZKs) are important primitives in cryptography. A major challenge since the early works on NIZKs has been to construct NIZKs with a statistical zero-knowledge guarantee against unbounded verifiers. In the common reference string (CRS) model, such "statistical NIZK arguments" are currently known from k-Lin in a pairing-group and from LWE. In the (reusable) designated-verifier model (DV-NIZK), where a trusted setup algorithm generates a reusable verification key for checking proofs, we also have a construction from DCR. If we relax our requirements to computational zero-knowledge, we additionally have NIZKs from factoring and CDH in a pairing group in the CRS model, and from nearly all assumptions that imply public-key encryption (e.g., CDH, LPN, LWE) in the designated-verifier model. Thus, there still remains a gap in our understanding of statistical NIZKs in both the CRS and the designated-verifier models.
In this work, we develop new techniques for constructing statistical NIZK arguments. First, we construct statistical DV-NIZK arguments from the k-Lin assumption in pairing-free groups, the QR assumption, and the DCR assumption. These are the first constructions in pairing-free groups and from QR that satisfy statistical zero-knowledge. All of our constructions are secure even if the verification key is chosen maliciously (i.e., they are "malicious-designated-verifier" NIZKs), and moreover, they satisfy a "dual-mode" property where the CRS can be sampled from two computationally indistinguishable distributions: one distribution yields statistical DV-NIZK arguments while the other yields computational DV-NIZK proofs. We then show how to adapt our k-Lin construction in a pairing group to obtain new publicly-verifiable statistical NIZK arguments from pairings with a qualitatively weaker assumption than existing constructions of pairing-based statistical NIZKs.
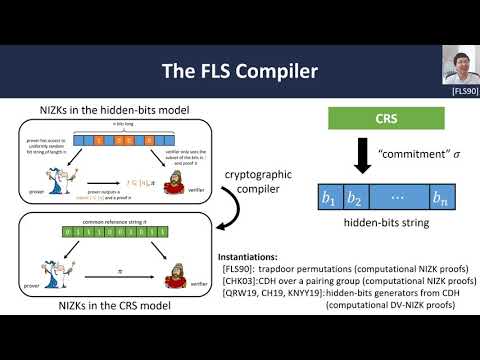
Our constructions follow the classic paradigm of Feige, Lapidot, and Shamir (FLS). While the FLS framework has traditionally been used to construct computational (DV)-NIZK proofs, we newly show that the same framework can be leveraged to construct dual-mode (DV)-NIZKs. |
Video from EUROCRYPT 2020
BibTeX
@inproceedings{eurocrypt-2020-30193,
title={New Constructions of Statistical NIZKs: Dual-Mode DV-NIZKs and More},
booktitle={39th Annual International Conference on the Theory and Applications of Cryptographic Techniques, Zagreb, Croatia, May 10–14, 2020, Proceedings},
series={Lecture Notes in Computer Science},
publisher={Springer},
keywords={non-interactive zero knowledge;NIZK;statistical zero-knowledge;designated-verifier;DV-NIZK},
volume={12105},
doi={10.1007/978-3-030-45727-3_14},
author={Benoît Libert and Alain Passelègue and Hoeteck Wee and David J. Wu},
year=2020
}